Самсон Хохотов - Formosa. Country of success
- Название:Formosa. Country of success
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:неизвестно
- Год:2022
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Самсон Хохотов - Formosa. Country of success краткое содержание
Formosa. Country of success - читать онлайн бесплатно ознакомительный отрывок
Интервал:
Закладка:
Самсон Хохотов
Formosa. Country of success

懷著極大的敬意, 向您推薦我的書。
略尽绵薄之力,
幫助國際友人更了解與認識台灣,
對台灣旅遊業的發展作出一點貢獻。
林巴虎


I dedicate this book to my friend Princess Michael of Kent, born Baroness Marie-Christine Anne Agnes Hedwig Ida von Reibnitz, who once helped me open a new page in my life.
Geography, Topography, Population and Language

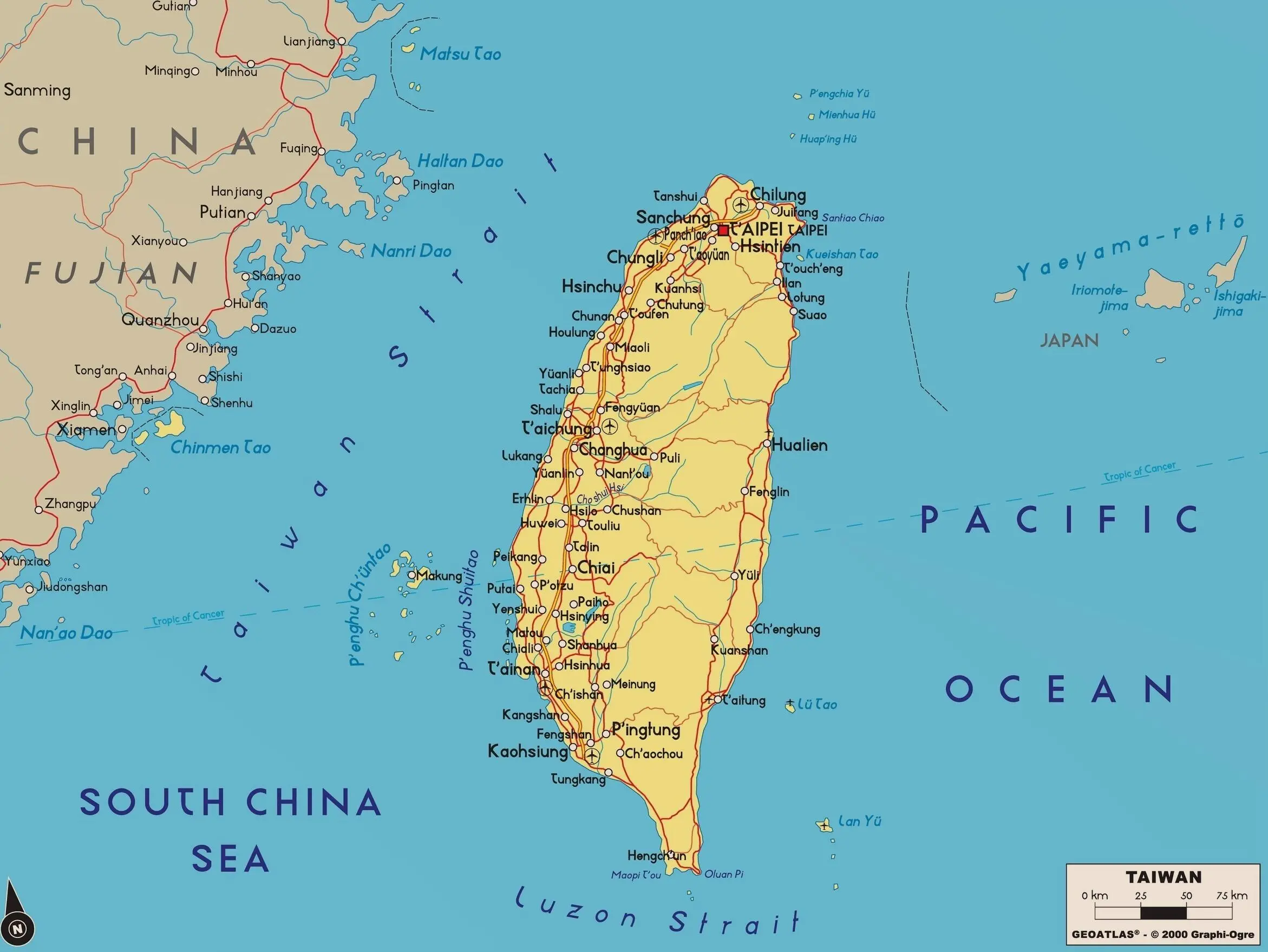
Taiwan is a large island located in the Pacific Ocean near the eastern coast of mainland China. Since 1949, it has been functioning as an independent state, the Republic
of China. The coast of Taiwan is washed by the East China Sea to the North, the South China Sea and the Philippine Sea to the South and the Pacific Ocean to the East.
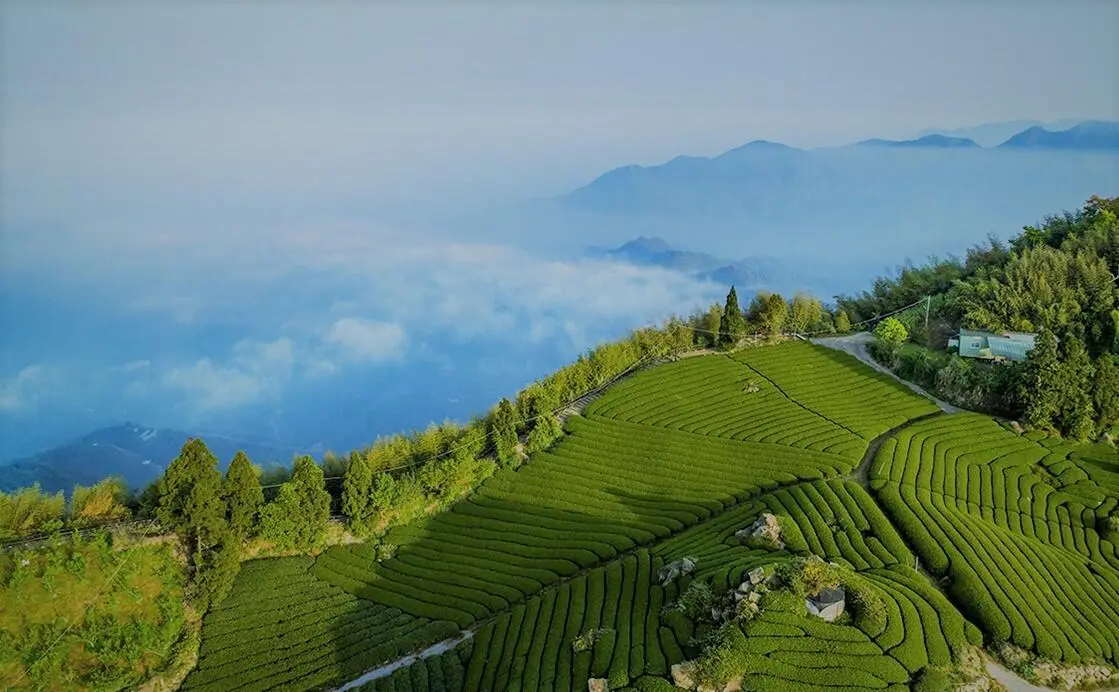
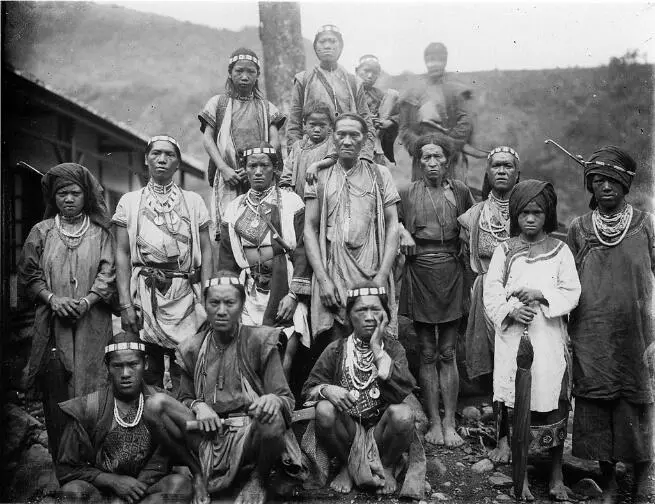
The island stretches for 394 km north to south, and is approximately 140 km across, giving an area of about 35,834 square kilometres. The length of the coastline is 1566 km. The eastern shores of the main island of Taiwan are steep, while in the west they are mostly flat with gently sloping plains. In the north, there are several (and, according to the latest updated information), dormant volcanoes. The Taiwan Mountains, covered with forests, stretch along the entire island. The highest of these is Mount Yushan at 3952m. In the west, there is a coastal plain and 90% of the island's population lives here. It is known that Aborigines lived in Taiwan about 10,000 years ago while, in contrast, the inhabitants of mainland China only began to settle in masse about 100 years ago. Today, about 10% of Taiwan residents speak the dialects of the Austronesian languages and these repre sent the indigenous population.

These aboriginal languages were once on the brink of extinction however, over the last 30 years or so, the authorities have been carefully preserving all ethnic groups of the population, actively helping them to develop the cultural heritage of their ancestors, and especially their languages.
An example of this is the people of the eastern coast of Taiwan who are called the Gaoshan.
There was a time when only a few living native speakers remained amongst the Gaoshan however the creation of a special Center for the Support of Ethnic Cultures
in 2000 has led to a complete revival of the language and this, in turn, has made it possible to open several radio and TV channels transmitting in the local dialect. Nowadays residents who speak a language belonging to the Austronesian family can easily switch to more widely used dialects while still retaining

their own. The dialect of most Taiwanese is
known as Hokhlo, the modern name for which is now Taiwan Hua or Guo Yu.
The Taiwan Hua dialects have their origin from the Fujian Province of China where this language group is known as Minnan Hua or Tai Yu.
Although Guo Yu was adopted as the country’s official language, about 70 per cent of the island's population use Tai Yu which is mainly spoken in the family circle and it also remains the language of communication within the framework of the village and other social communities.
While Tai Yu has no official status it can widely be found on subways and advertisements in the capital as well as in some non-state newspapers, books, online publications and shop window inscriptions.
When it comes to written language the people of Taiwan use traditional Chinese characters in addition to a Zhu Yin

writing system developed by Western philologists and which is based on the Latin alphabet. There is also another language, that is very different from the usual Chinese. To
some, it may seem similar to the Cantonese dialect and there
are several million native speakers of this dialect of Chinese left.
It is called the Hakka language and its speakers belong to a Chinese clan group. This name is translated as "guest". The endurance and self-confidence of these people were shaped and further developed by their long travels and wanderings among hostile tribes back home in northern China. The proximity to Fujian ensured that many people from here, which has a considerable population of Hakka, migrated to Taiwan.
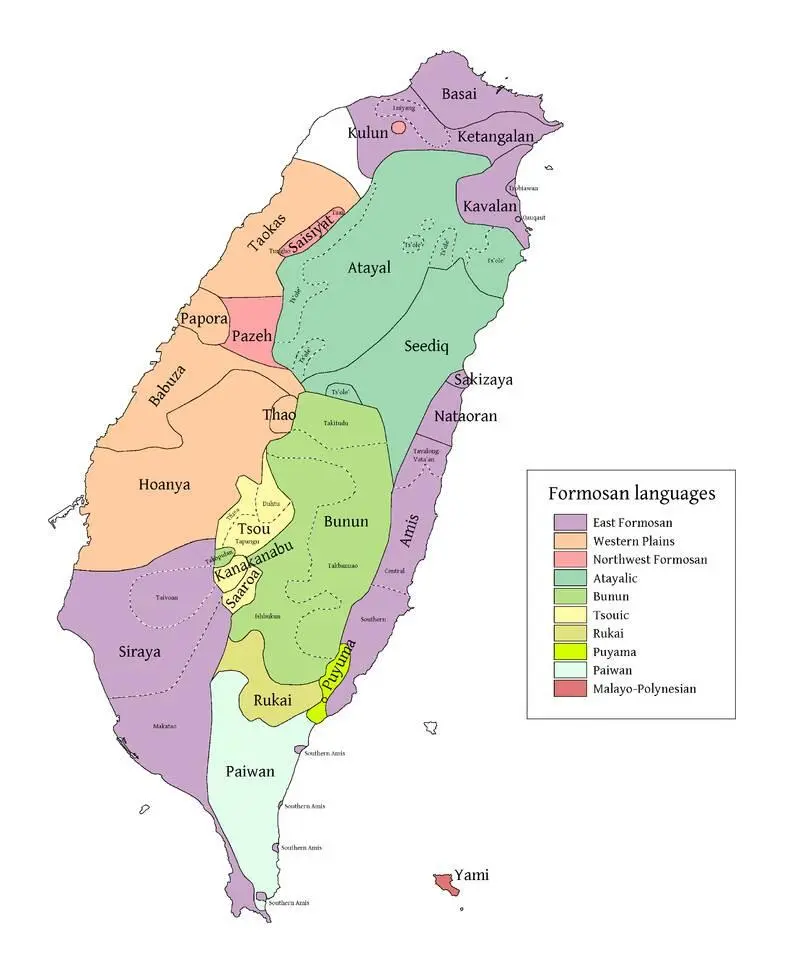
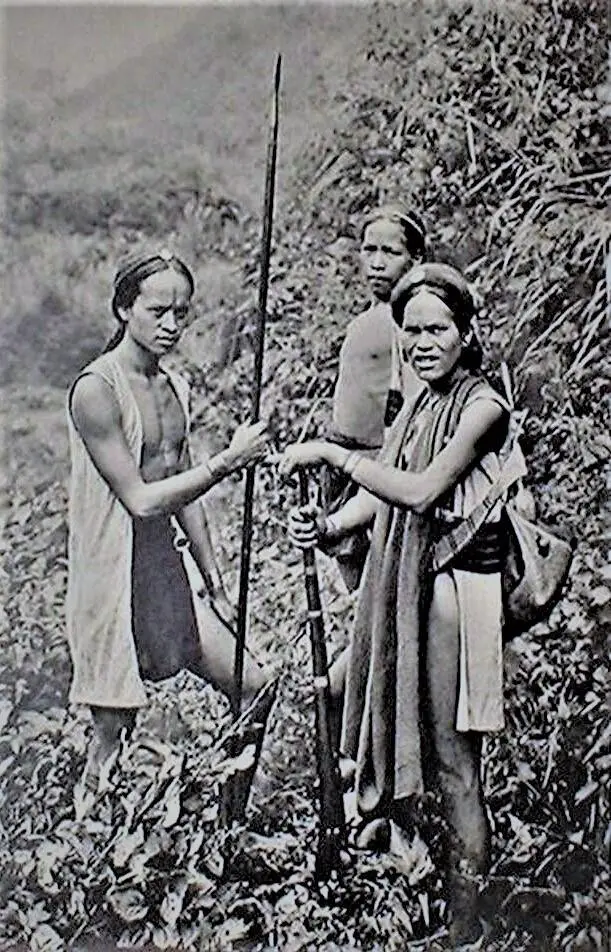
Until 1945, Japanese was the official language in Taiwan and taught in schools. But after the end of World War II in 1945, Guo Yu became the official language and began to be taught in schools. The hill tribes speak the Taiwanese languages of the Austronesian family and Guo Yu, while the lowland Taiwanese completely switched over to Guo Yu. The indigenous population of Taiwan of Austronesian origin includes the Aborigines, whose total number is about 550,000 people. Plains Aborigines can be found in the west and north of Taiwan, while Mountain Aborigines inhabit the central and southern parts of the island and the eastern plains.
These have mostly preserved their original culture and languages.
According to official data, plains tribes (from south to north)
:
Siraya
Mattauw
Soelangh
Baccloangh
Sinckan
Taivoan
Hoanya
Lioa
Arikun
Babuza
Papora
Pazeh
Taokas
Ketangalan (Luilan)
Basai
Kaukaut
Trobivan
Kavalan (Cabaran)
Hill tribes include (from north to
South):
Saysiyat
Atayal
Truku (Taroko or Sedek)
Thao
Tzou
Kanakhabu
Saaroa
Bunun
Rukai
Ami (Pantsakh)
Puyuma
Paiwan
Officially, Yami (Taoist) is also referred to as Gaoshan. Yami live on a small island of Lanyu South-East of Taiwan. They speak the Austronesian language Yami, which resembles the Filipino language, Tagalog.
History of settlement
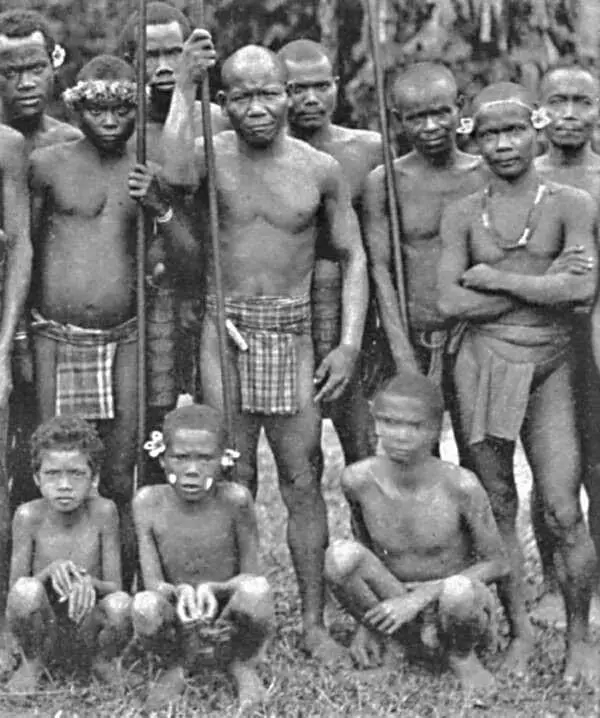

The history of Taiwan, with the appearance of the first humans, goes back as far as the
Upper Paleolithic period.
In the Taiwan Strait, near the Pescadores Islands (the Penghu Islands), fishermen fished out the jaw of an ancient man who belonged to the species Homo erectus. The first humans appeared in Taiwan around 50,000 BC. Some scientists claim the Negro-Australoids to be the first settlers in Taiwan since the Paleolithic, regarding archaeological and
has disappeared over time. Almost simultaneously with the Negroids, the Indonesians settled in Taiwan. The  Austronesians are believed to have reached Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula, Northeast China and Japan by sea.
Austronesians are believed to have reached Taiwan, the Korean Peninsula, Northeast China and Japan by sea.
Scientists generally believe that Java and Sulawesi provided the principal source of Austronesian migration. Additionally, Oceania is another source of migration, as evidenced by the megaliths at the eastern coast of Taiwan and anthropological observations.
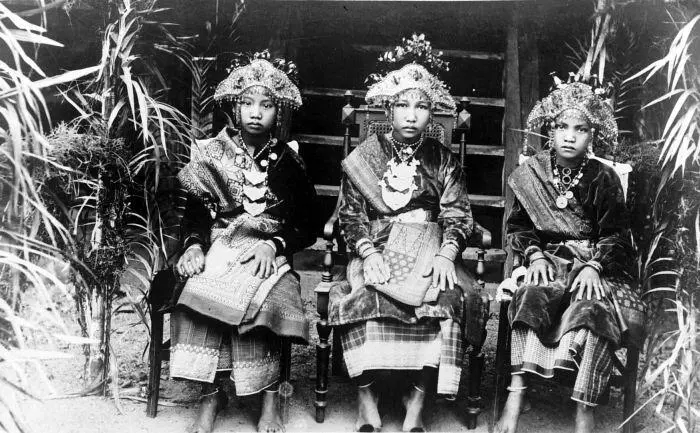

The resettlement was not simultaneous but occurred in waves throughout the Neolithic period, as evidenced by the Corded Ware finds. Recently, researchers have concluded that both processes took place in Taiwan migration and autochthonous development. The migrants had adapted to the new conditions, and their descendants became aborigines.
The earliest archaeological culture in Taiwan was the Changbin culture, named after the place of finds in the east of Taiwan. Sites of ancient Taiwanese have also been located in other locations in Taiwan, especially in Tainan County and in
the Taipei Basin. Most likely, they were representatives of the Australoid race and inhabited all of Southeast Asia between 10 and 45 thousand years ago.
It is Taiwan that is the ancestral home of the Austronesian languages. In around 8000 years B.C. and as evidenced by archaeological finds, Austronesian native-speakers initially migrated from the east coast of China to Taiwan.
Native speakers of these languages only later, according to the data of historical linguistics, began to migrate from the island of Taiwan by sea throughout Oceania. This migration is understood to have started about 6,000 years ago and occurred in several stages. Taiwan's Neolithic past is the Dabenken culture (2700-5000 BC).
The first Taiwanese crops were yams and taro. From the 2nd millennium B.C., the natives of Taiwan began to breed dogs and pigs. The oldest evidence of life in Taiwan is the skeleton of a young woman with a child in her arms found near the city of Taichung. Following scientific analysis, the age of the fossils is around 4800 years, and therefore they belong to the Neolithic era. The earliest mention of the island of Taiwan was in Chinese sources of the 3rd century BC. This information is, however, very scarce. The Chinese, being close neighbours, were in no hurry to colonize the island.
By the third century, when life on the island was relatively- well established, military expeditions by the Chinese began. Crafts had developed, and agricultural plants grew. The early Iron Age on the island, represented by the Jingpu culture, dates back to the 1st millennium BC.
Over time, the local ceramic pottery tradition disappeared. Local craftsmen learned how to make products from porcelain and metal. The Taiwanese achieved sophistication in the production of copper bells that scare away evil spirits.
And in the 1st millennium AD, iron knives and spearheads are already appearing. These items belong to the Nyaosun culture.
Production of plain red-brown ceramics (without ornaments) begins.
The development of navigation, characteristic of the rest of the Austronesians, fades into the background, while the development of the island is becoming the main priority in the life of the Taiwanese. Despite the difficulties, little by little the Taiwanese natives selflessly mastered even the remote mountainous regions.
The ancient Chinese chronicles Hou Han Shu and San Go Zhi contain the first mentions of an island called Yizhou (the island of the barbarians).
Since the Sui period (years 581 through 618), Taiwan is more often called Lucyu (after the name of a small kingdom in the southwestern part of the island).
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:






![Ирина Хакамада - Success [успех] в Большом городе](/books/1140519/irina-hakamada-success-uspeh-v-bolshom-gorode.webp)



