Фред Адамс - Пять возрастов Вселенной
- Название:Пять возрастов Вселенной
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:Институт компьютерных исследований; R&C Dynamics
- Год:2006
- Город:Ижевск
- ISBN:5-93972-500-7
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Фред Адамс - Пять возрастов Вселенной краткое содержание
В конце двадцатого века Фред Адамс и Грег Лафлин завладели вниманием всего мира, выделив пять временных эпох. Этих авторов считают создателями долгосрочного проекта эволюции Вселенной. Масштабы их творения, охватившего полную историю космоса от его рождения до гибели, и глубина рассмотренных научных вопросов внушают благоговейный трепет. Однако «Пять возрастов Вселенной» — не просто справочник, описывающий физические процессы, которые руководили нашим прошлым и будут формировать наше будущее, это истинная эпопея. С ее помощью можно совершить фантастическое путешествие в физику вечности, не покидая Земли. Это единственная биография Вселенной, которая вам когда-либо понадобится.
Книга предназначена для широкого круга читателей.
Пять возрастов Вселенной - читать онлайн бесплатно полную версию (весь текст целиком)
Интервал:
Закладка:
Hawking S.W., D.N. Page and C.N. Pope, 1979, The propagation of particles in spacetime foam, Phys. Lett. 86 B, 175.
Helmholz H. von, 1854, On the Interaction of Natural Forces.
Hooft G., 1976, Symmetry breaking through Bell-Jackiw anomalies, Phys. Rev. Lett. 37, 8.
Hubbell J.H., H.A. Grimm and I. Overbo, 1980, Pair, triplet, and total atomic cross sections for 1 MeV-100 GeV photons in elements Z= 1 to 100, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 9, 1023.
Hut P. and M.J. Rees, 1983, How stable is our vacuum? Nature 302,508.
Islam J.N., 1977, Possible ultimate fate of the universe, Quart. J. R. Astron. Soc. 18, 3.
Islam J.N., 1979, The ultimate fate of the universe, Sky and Telescope 57, 13.
Islam J.N., 1983, The Ultimate Fate of the Universe (Cambridge: Cambridge Univ Press).
Jungman G., M. Kamionkowski and K. Griest, 1996, Supersymmetric dark matter, Physics Reports 267, 195.
Kane G.L., 1993, Modern Elementary Particle Physics (Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley).
Kane G.L., 1995, The Particle Garden (Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley).
Kant I., 1755, Allegmeine Naturgeschichte und Theorie des Himmels.
Kennicutt R.C., P. Tamblyn and C.W. Congdon, 1994, Past and future star formation in disk galaxies, Astrophys. J. 435, 22.
Kippenhahn R. and A. Weigert, 1990, Stellar Structure and Evolution (Berlin: Springer).
Knickerbocker W.S., 1927, Classics of Modern Science (Boston: Beacon Press).
Kolb E.W. and M.S.Turner, 1990, The Early Universe (Redwood City, CA: Addison- Wesley).
Kormendy J., et al., 1997, Spectroscopic evidence for a supermassive black hole in NCG 4486B, Astrophys. J. 482, L139.
Krauss L., 1986, Dark matter in the universe, Scientific American 255, 58.
Krauss L.M., M. Srednicki and F. Wilczek, 1986, Solar system constraints and signature for dark matter candidates, Phys. Rev. D 33, 2079.
Langacker P., 1981, Grand unified theories and proton decay, Physics Reports 72, 186.
Laplace P.S., 1796, Exposition du systeme du monde (Paris).
Laughlin G. and F.C. Adams, 1998, The modification of planetary orbits in dense stellar clusters, Astrophys. J. Lett. 508, L171.
Laughlin G., P. Bodenheimer and F.C. Adams, 1997, The end of the main sequence, Astrophys. J. 482, 420.
Lightman A.P. and S.L. Shapiro, 1978, The dynamical evolution of globular clusters, Rev. Mod. Phys. 50, 437.
Linde A.D., 1982, A new inflationary universe scenario: A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy, and primordial monopole problems, Phys. Lett. 108 B, 389.
Linde A.D., 1983a, Chaotic inflation, Phys. Lett. 129 B, 177.
Linde A.D., 1983b, Decay of the false vacuum at finite temperature, Nucl. Phys. B216, 421.
Linde A.D., 1986, Eternally existing self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe, Phys. Lett. 175B, 395.
Linde A.D., 1988, Life after inflation, Phys. Lett. 211 B, 29.
Linde A.D., 1989, Life after inflation and the cosmological constant problem, Phys. Lett. 227 B, 352.
Linde A.D., 1990, Particle Physics and Inflationary Cosmology (New York: Harwood Academic).
Linde A., 1994, The self-reproducing inflationary universe, Scientific American 271, 48.
Loh E. and E. Spillar, 1986, A measurement of the mass density of the universe, Astrophys. J. Lett. 307, LI.
Manchester R.N. and J.H. Taylor, 1977, Pulsars (San Francisco: W. H. Freeman).
Marcy G.W. and R.P. Butler, 1996, A planetary companion to 70 Virginis, Astrophys. J. Lett. 464, L147.
Marcy G.W. and R.P. Butler, 1998, Detection of extrasolar giant planets, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 36, 57.
Mayor M. and D. Queloz, 1995, A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star, Nature 378, 355.
Meyer S.S., E.S. Cheng and L.A. Page, 1991, A measurement of the large-scale cosmic microwave background anisotropy at 1.8 millimeter wavelength, Astrophys. J. Lett. 410, L57.
Mihalas D. and J. Binney, 1981, Galactic Astronomy: Structure and Kinematics (New York; W. H. Freeman).
Miller G.E. and J.M. Scalo, 1979, The initial mass function and stellar birthrate in the solar neighborhood, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 41, 513.
Misner C.W., K.S. Thorne and J.A. Wheeler, 1973, Gravitation (San Francisco: W. H. Freeman).
Mohapatra R.N. and R.E. Marshak, 1980, Local B-L symmetry of electroweak interactions, Majorana neutrinos, and neutron oscillations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 44, 1316.
Narayan R., D. Barret and J.E. McClintock, 1997, Advection-dominated accretion model of black hole V404 Cygni in quiescence, Astrophys. J. 482, 448.
Ohanian H.C. and R. Ruffini, 1994, Gravitation and Spacetime (New York: W. W. Norton).
Oppenheimer B.R., S.R. Kulkarni, К. Matthews and Т. Nakajima, 1995, The infrared spectrum of the cool brown dwarf G1229B, Science 270, 1478.
Page D.N., 1980, Particle transmutations in quantum gravity, Phys. Lett. 95 B, 244.
Page D.N. and M.R. McKee, 1981a, Matter annihilation in the late universe, Phys. Rev. D 24, 1458.
Page D.N. and M.R. McKee, 1981b. Eternity matters, Nature 291, 44.
Pais A., 1986, Inward Bound (Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press).
Particle Data Group, 1998, Particle physics booklet, European Phys. J. C3, 1.
Peebles P.J.E., 1993, Principles of Physical Cosmology (Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press).
Peebles P.J.E., 1994, Orbits of nearby galaxies, Astrophys. J. 429, 43.
Penzias A.A. and R.W. Wilson, 1965, A measurement of excess antenna temperature at 4080 Mc/s, Astrophys. J. 142, 419.
Perkins D., 1984, Proton decay experiments, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 34, 1.
Poundstone W., 1985, The Recursive Universe (New York: Morrow).
Press W.H. and D.N. Spergel, 1985, Capture by the Sun of a galactic population of weakly interacting massive particles, Astrophys. J. 296, 679.
Primack J.R. and M.Sher, 1980, Photon mass at low temperature, Nature 288, 680.
Rajaraman R., 1987, Solitons and Instantons (Amsterdam: North-Holland).
Rana N.C., 1991, Chemical evolution of the galaxy, Ann. Rev Astron. Astrophys. 29, 129.
Rees M.J., 1969, The collapse of the universe: An eschatological study, Observatory 89, 193.
Rees M.J., 1981, Our universe and others, Quart. J. R. Astron. Soc. 22, 109.
Rees M.J., 1984, Black hole models for active galactic nuclei, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 22, 471.
Rees M.J., 1997, Before the Beginning: Our Universe and Others (Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley).
Riess A.G., W.H. Press and R.P. Kirshner, 1995, Determining the motion of the local group using type la supernova light curve shapes, Astrophys. J. Lett. 438, L17.
Russo J.G., L. Susskind and L. Thorlacius, 1992, End point of Hawking radiation, Phys. Rev. D 46, 3444.
Sackmann I.-J., A.I. Boothroyd and K.E. Kraemer, 1993, Our Sun III: Present and future, Astrophys. J. 418, 457.
Sakharov A.D., 1967, Violation of CP invariance, С asymmetry and baryon asymmetry of the universe, JETP Letters 5, 24.
Salpeter E.E., 1955, The luminosity function and stellar evolution, Astrophys. J. 121, 161.
Salpeter E.E. and H.M. van Horn, 1969, Nuclear reaction rates in high densities, Astrophys. J. 155, 183.
Sato K., H. Kodama, M. Sasaki and K. Maeda, 1982, Multiproduction of universes by first order phase transition of a vacuum, Phys. Lett. 108 B, 103.
Scalo J.M., 1986, The stellar initial mass function, Fund. Cos. Phys. 11, 1.
Schopf J., 1992, editor, Major Events in the History of Life (Boston: Jones and Bartlett).
Schuster J., et al., 1993, Cosmic background radiation anisotropy at degree scales: Further results from the South Pole, Astrophys. I. Lett. 412, L47.
Shapiro S.L. and S.A. Teukolsky, 1983, Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects (New York: Wiley).
Sher M., 1989, Electroweak Higgs potentials and vacuum stability, Physics Reports 179, 273.
Shu F.H., 1982, The Physical Universe (Mill Valley, CA: University Science Books).
Shu F.H., F.C. Adams and S. Lizano, 1987, Star formation in molecular clouds: Observation and theory, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 25, 23.
Smolin L., 1997, Life of the Cosmos (New York: Oxford Univ. Press).
Smoot G., et al., 1992, Structure in the СОВЕ differential microwave radiometer first-year maps, Astrophys. J. Lett. 396, LI.
Spooner N.J.C., 1997, editor, The Identification of Dark Matter (London: World Scientific).
Steinhardt P.J. and M. S. Turner, 1984, A prescription for successful new inflation, Phys. Rev. D 29, 2162.
Stevenson D.J., 1991, The search for brown dwarfs, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 29, 163.
Suzuki M., 1988, Slightly massive photon, Phys. Rev. D 38, 1544.
Thorne К.S., R.H. Price and D.A. MacDonald, 1986, Black Holes: The Membrane Paradigm (New Haven: Yale Univ. Press).
Thorne K.S., 1994, Black Holes and Time Warps: Einstein's Outrageous Legacy (New York: Norton).
Timmes F.X., 1996, unpublished calculations.
Tinney C.G., 1995, editor, The Bottom of the Main Sequence and Beyond (Berlin: Springer).
Tipler F.J., 1992, The ultimate fate of life in universes which undergo inflation, Phys. Lett. 286 B, 36.
Tolman R.C., 1934, Relativity, Thermodynamics, and Cosmology (Oxford: Clarendon Press).
Turner M.S., 1983, The end may be hastened by magnetic monopoles, Nature 306, 161.
Turner M.S. and F. Wilczek, 1982, Is our vacuum metastable? Nature 298, 633.
Turok N., 1997, editor, Critical Dialogues in Cosmology (Singapore: World Scientific).
Vilenkin A., 1983, Birth of inflationary universes, Phys. Rev. D 27, 2848.
Visser M., 1995, Lorentzian Wormholes: From Einstein to Hawking (Woodbury, NY: AIP Press).
Voloshin M.В., I.Yu. Kobzarev and L.B. Okun, 1975, Bubbles in metastable vacuum, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 20, 644.
Wagoner R., 1973, Big bang nucleosynthesis revisited, Astrophys. J. 179, 343.
Wald R.M., 1984, General Relativity (Chicago: Univ. Chicago Press).
Wald R.M., 1994, Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime and Black Hole Thermodynamics (Chicago: Univ. Chicago Press).
Walker T.P., G.Steigman, D.N. Schramm, K.A. Olive and H.-S.Kang, 1991, Primordial nucleosynthesis redux, Astrophys. J. 376, 51.
Weinberg M.D., 1989, Self-gravitating response of a spherical galaxy to sinking satellites, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 239, 549.
Weinberg S., 1972, Gravitation and Cosmology (New York: Wiley).
Weinberg S., 1977, The First Three Minutes (New York: Basic).
Weinberg S., 1978, A new light boson? Phys. Rev. Lett. 40, 223.
Weinberg S., 1980, Varieties of baryon and lepton nonconservation, Phys. Rev. D 22, 1694.
Weinberg S., 1989, The cosmological constant problem, Rev. Mod. Phys. 61, 1
Weinberg S., 1995, Quantum Theory of Fields (Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press).
Wilczek F. and A. Zee, 1979, Conservation or violation of B-L in proton decay, Phys. Lett. 88 B, 311.
Wood M.A., 1992, Constraints on the age and evolution of the galaxy from the white dwarf luminosity function, Astrophys. J. 386, 539.
Wright E.L., et al., 1992, Interpretation of the cosmic microwave background radiation anisotropy detected by the СОВЕ differential microwave radiometer, Astrophys. J. Lett. 396, L13.
Zel'dovich Ya.В., 1976, A new type of radioactive decay: Gravitational annihilation of baryons, Phys. Lett. 59 A, 254.
Zuckerman B. and M.A. Malkan, 1996, editors, The Origin and Evolution of the Universe (Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett).
Ключевые события в биографии Вселенной
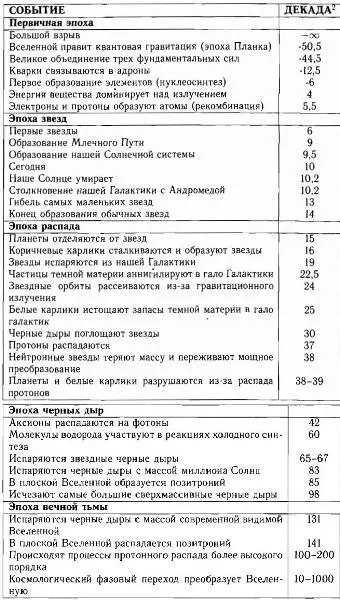
1
Интервал:
Закладка:










