Alexander Akulov - Manual of comparative linguistics
- Название:Manual of comparative linguistics
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:Array Литагент «Ридеро»
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:9785447441906
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Alexander Akulov - Manual of comparative linguistics краткое содержание
Manual of comparative linguistics - читать онлайн бесплатно ознакомительный отрывок
Интервал:
Закладка:
Slavonic group
Czech 0.52 (calculated after Harkins 1952)
Polish 0.57 (calculated after Swan 2002)
Celtic group
Irish 0.67 (McGonage 2005)
Welsh 0.35 (calculated after King 2015)
Roman group
Latin 0.26 (calculated after Bennet 1913)
Spanish 0.34 (calculated after Kattán-Ibarra, Pountain 2003)
2.1.4.3. PAI of languages of Afroasiatic stock
Semitic group
Central Semitic subgroup
Arabic (Classical) 0.26 (calculated after Yushmanov 2008)
Phoenician 0.26 (calculated after Shiftman 2010)
Eastern Semitic subgroup
Akkadian (Old Babylonian dialect) 0.2 (calculated after Kaplan 2006)
Egypt group
Coptic (Sahidic dialect) 0.87 (calculated after Elanskaya 2010)
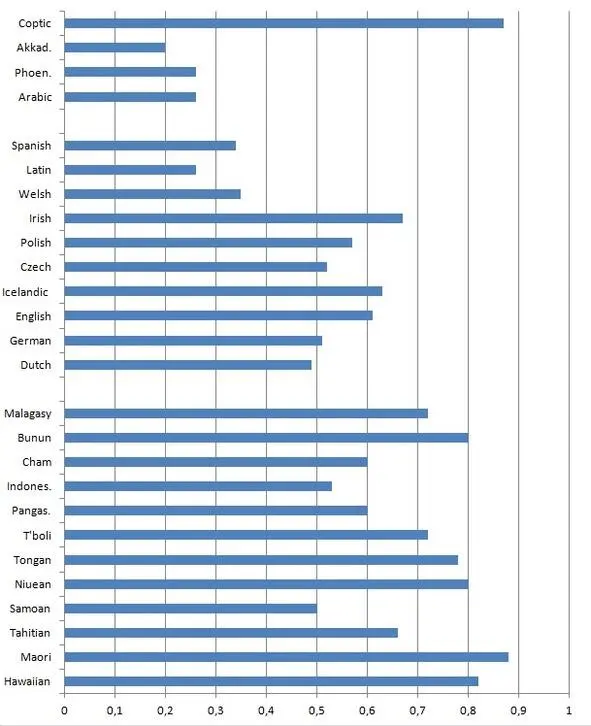
Pic. 3. Diagram representing PAI values of some firmly assembled stocks
2.1.5. PAI of a group/stock
PAI of a group or a stock can be calculated as arithmetical mean and it’s quite precise for rough estimation.
One can probably say that just arithmetic mean is quite rough estimation and in order to estimate PAI in a more precise way it would be better to take values of PAI of particular languages with coefficients that show proximity of particular languages to the ancestor language of the stock. Coefficient of proximity is degree of correlation of grammar systems.
Let’s test this hypothesis and see whether it so.
For instance, in the case of Austronesian it would be somehow like the following:
Malagasy^PAN 9 9 PAN means Proto-Austronesian; “^” is sign of grammar/structure correlation
≈ 0.5;
Bunun^PAN ≈ 0.8;
Philippine group^PAN ≈ 0.7;
Indonesian^PAN ≈ 0.6;
Cham^PAN ≈ 0.4;
Polynesian languages^PAN ≈ 0.5.
Indexes show degree of proximity of languages (grammatical systems). In current case these indexes are not results of any calculations but just approximate speculative estimation of degrees of proximity of modern Austronesian languages with Proto-Austronesian; it is supposed that Formosan languages and so called languages of Philippines type are the closest relatives of PAN among modern Austronesian.
If we take each particular PAI value with corresponding coefficient of proximity we get that PAI of Austronesian is about 0.44.
If we take just arithmetical mean without proximity coefficients we get 0.6.
0.6 is obviously closer to real values of PAI of Austronesian languages than 0.44. Hence thereby it’s possible to state that just arithmetical mean is completely sufficient way to calculate PAI of a group/stock while PAI calculated with use of proximity coefficients gives results that differ seriously from reality.
2.1.6. PAI in diachrony
It can be supposed that PAI doesn’t change much in diachrony.
PAI of Late Classical Chinese is 0.5 (calculated after Pulleyblank 1995).
PAI of Contemporary Mandarin is 0.5. (calculated after Ross, Sheng Ma 2006).
PAI of Early Old Japanese is 0.13 (calculated after Syromyatnikov 2002).
PAI of contemporary Japanese is 0.13 (calculated after Lavrent’yev 2002).
Probably it should be also tested on other examples but even on the material of these examples we can see that PAI of a language is same in different stages of its history.
2.1.7. Summary of PAI method
One can probably say that Coptic has broken our hypothesis, but actually PAI just has shown us that group of Coptic language and Semitic group diverged very long ago, probably in Neolithic epoch yet.
However, the tests have shown that values of PAI of related languages are actually rather close, i.e.: they do not differ more than fourfold (pic. 3).
Thus, it is possible to say that PAI is something alike safety valve of comparative linguistics: if its values don’t differ more than fourfold then PAI has no distinction ability and actually there are no obstacles for further search for potential genetic relationship; but if values of PAI differ fourfold and more, then should be found absolutely ferroconcrete proves of genetic relationship.
Also I am specially to note that PAI method doesn’t require estimation of measurement error as far as PAI allows fourfold gap of values.
2.2. Why is it possible to prove that languages are not related?
2.2.1. Root of problem is changing of concepts
One can probably say that it is impossible to prove unrelatedness of two languages so I am to make some explanation on why it is possible.
In contemporary comparative linguistics there is a weird presupposition that it is impossible to prove that certain languages are not genetically related. As I can understand this point of view was inspired by Greenberg as well as some other obscurantist ideas of contemporary historical linguistics. It seems quite weird that it is possible to prove relatedness but it is not possible to prove unrelatedness. Let’s check whether it is so.
First of all, I am to note that statement about impossibility of proving unrelatedness is actually sophism based on changing of concepts, i.e.: when they speak about proves of relatedness then relatedness means “to belong to the same stock” and it is regular and normal meaning of the concept of relatedness in linguistics; however, when they speak about unrelatedness then meaning of relatedness suddenly changes: they start to suppose that actually all existing languages are related since they are supposed to be derivates of same proto-language that existed in a very distant epoch in past and due to this fact we can’t prove unrelatedness but can just state that a language doesn’t belong to a stock.
2.2.2. Concepts of relatedness and unrelatedness from the point of view of other sciences
In order to clear the meaning of the concept of relatedness it’s useful to pay some attention to other sciences where this concept also is used. If we take a look at, for instance: biology, physics or technical sciences we can see that many items are distributed by classes/classified despite they obviously have common origin; and considering them it is completely normal to speak about relatedness and unrelatedness. All being have common origin and so they all are relatives in a very deep level but this fact doesn’t mean they cannot be classified into kingdoms, phylums, classes, orders, suborders, families, subfamilies; the fact that ant, bear, pine tree, whale, sparrow have common ancestor doesn’t mean it is impossible to distinguish bear from whale and whale from pine tree.
However, as far as languages aren’t self replicating systems like biological systems and are closer to artifacts so any parallels between biological systems and language always should be made with certain degree of awareness since they are more allegories than analogies while correlations between languages and some artificial items are more precise, for instance: all existing cars are derivates of steam engine that existed in the middle of 19 thcentury, but it doesn’t mean we can’t classify cars/engines and speak of relatedness and unrelatedness of certain types.
These examples evidently show us the following:
1) When they say about an item that is related with another it means “they both belong to the same class”.
2) It is possible to speak about relatedness and unrelatedness of certain items even though all classes of them have common origin.
2.2.3. Concepts of relatedness and unrelatedness from point of view of set theory and abstract algebra
Concept of relatedness is actually equivalence relation since it meets necessary and sufficient requirements for a binary relation to be considered as equivalence relation:
1) Reflexivety: a ~ a: a is related with a;
2) Symmetry: if a ~ b then b ~ a: if a is related with b then b is related with a;
3) Transitivity: if a ~ b and b ~ c then a ~ c: if a is related with b and b is related with c then a is related with c.
If an equivalence relation is defined on a set then it necessarily supposes grouping of elements of the set into equivalence classes and these classes aren’t intersected (Hrbacek, Jech: 1999).
2.2.4. Particular conclusions on the concepts of relatedness and unrelatedness for linguistics
When it is said that certain languages are genetically related (or simply related) it means that these languages belong to the same stock or even to the same group.
Taking into the consideration what has been said in 2.2.2 we should keep in mind that in the case of languages there are actually no positive evidences that all languages existing nowadays originated from the same ancestor, i.e.: monogenesis is still an unproved hypothesis, though anyway even if all languages can be reduced to the same proto-language that existed in a very distant past it doesn’t mean yet we can’t speak of their relatedness/unrelatedness.
Then, taking into consideration what has been said in 2.2.3 we can say the following:
The set of languages existing nowadays on the planet is rather well described: we know that there are about 7102 languages and about 151 stocks and 83 isolated languages (Ethnologue: 2015), so we can speak about 234 stocks; and we hardly can expect discovering of some new unknown languages. Thus, we can say that we have rather complete image of set of languages and that there are about 234 classes of equivalence/relatedness.
If we take an X stock, we obviously can show many languages which don’t belong to the stock, i.e.: languages which are not related with language x (a random language of X stock), for example: in the case of Indo-European stock there are many languages which are not related with English: Arabic, Basque, Finnish, Georgian, Turkish, Chinese, Japanese, Hawaiian, Eskimo, Quechua and so on. In the case of Sino-Tibetan stock there are many languages which aren’t related with Chinese: Arabic, English, Eskimo, Finnish, Japanese, Turkish, Vietnamese and so on.
Thus, we can conclude the following:
1) Relatedness means “language belongs to a stock” unrelatedness means “language doesn’t belong to a stock”.
2) If set of 234 classes/stocks has been set up then it obviously supposes that there should be a possibility of classification, i.e.: we can say whether a language belongs to a stock; moreover, we always can show some languages which don’t belong to the stock. If possibility to prove unrelatedness is denied then we actually can’t establish scopes of stocks and can’t distinguish one stock from another; then even a single stock hardly could have been assembled.
3) Any two randomly chosen languages can be related or not related, i.e.: there can be no “third variant” since relatedness/unrelatedness supposes the existence of classes which don’t intersect. If a language of X stock is related to a language of Y stock it means that these stocks are related.
4) Possible objection can be the following: one can probably say that it is impossible to make precise conclusions in linguistics. Actually, I don’t think someone can seriously say this, however, if someone would speak out something like this I can only point on the fact that very long ago people thought that precise conclusions are impossible in physics. Possibility of precise estimations and precise conclusions depends on scholars’ will and on scholars’ intellectual courage only, but not on material itself; any material can be represented as item that can’t be formalized, and many items have already been successfully formalized.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:










