Я. Ившин - Metal Corrosion. Electroplating (Защита от металлов от коррозии. Гальванотехника)
- Название:Metal Corrosion. Electroplating (Защита от металлов от коррозии. Гальванотехника)
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:Литагент БИБКОМ
- Год:2013
- Город:Казань
- ISBN:978-5-7882-1386-6
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Я. Ившин - Metal Corrosion. Electroplating (Защита от металлов от коррозии. Гальванотехника) краткое содержание
Metal Corrosion. Electroplating (Защита от металлов от коррозии. Гальванотехника) - читать онлайн бесплатно ознакомительный отрывок
Интервал:
Закладка:
9 . Give English equivalents to the following word combinations and learn them by heart:
сопротивляться коррозионному воздействию среды
металлы и сплавы
коррозионное разрушение поверхности
объем разрушенного металла
расплавы электролитов
действие радиоактивного излучения
жизнедеятельность микроорганизмов
радиационная коррозия
10 . Give Russian equivalents to the following word combinations and learn them by heart:
chloride ions
oxygen concentration
electrochemical reactions
wall thickness of a metal
wet corrosion
corrosion resistance
nonelectrolyte
ground corrosion
11 . Translate the following sentences into Russian.
1. Uniform corrosion is considered the form of corrosion that can be tolerated in marine structures and equipment.
2. Crevice corrosion occurs at places with gaskets, bolts and lap joints where crevice exists.
3. Pitting corrosion can be prevented through proper selection of materials with known resistance to the service environment.
4. The reaction starts at the surface and proceeds uniformly.
5. The gap or crevice can be formed between two metals or a metal and non-metallic material.
6. The most severe attack occurs at the joint between the two dissimilar metals.
7. Copper produces a green film of corrosion product containing hydrated sulphate, or carbonate, or chloride.
8. Pipelines or tanks that are exposed to an electrolyte with a low oxygen concentration are generally anodic to the same material exposed to an electrolyte with a high oxygen content.
9. Localized corrosion can be defined as selective removal of metal by corrosion at small special areas or zones on a metal surface in contact with a liquid environment.
10. The process of corrosion requires four elements: an anode, a cathode, an electrolyte, and a metallic path.
12 . Translate the following sentences into English.
1. Коррозия металлических сооружений наносит большой материальный и экономический ущерб.
2. Коррозия металлов бывает сплошной и местной.
3. Человечество несет огромные материальные потери в результате коррозии трубопроводов, деталей машин, судов, мостов, морских конструкций и технологического оборудования.
4. Наибольшую чувствительность к щелевой коррозии проявляют пассивные металлы в случае возможной их депассивации в щелях.
5. Наиболее распространенным и практически важным видом химической коррозии является газовая коррозия – коррозия металлов в сухих газах (воздух, продукты сгорания топлива) при высоких температурах.
6. Процессы окисления металла и восстановления окислительного компонента протекают раздельно в среде жидкого электролита.
7. Язвенная коррозия часто наблюдается у нержавеющих стальных сплавов.
8. Если водород не выделяется, происходит восстановление кислорода, и здесь говорят о кислородной коррозии, или коррозии с кислородной деполяризацией.
9. Коррозионное сопротивление нержавеющей стали зависит от тонкого невидимого пассивного слоя на стальной поверхности.
10. Этот слой состоит главным образом из хромированной окиси, которая формируется в реакции с кислородом содержащимся в воздухе.
13 . Translate the following word combinations.
Uniform corrosion – гальваническая коррозия – crevice corrosion – концентрационная коррозия – graphitic corrosion – подземная коррозия – electrolyte – окисление – corrosion resistance – медь – metal surface – коррозийное воздействие – oxygen concentration – распространение – gasket – процессы окисления – oxidizing component – сухой газ.
14 . Give the definitions of the words and word combinations.
1. Depolarization is …
2. Passive metals are …
3. Metallography is …
4. Liquid is …
5. Temperature is …
15 . Give the example(s) of the uniform corrosion.
16 . Answer the following questions using texts from Unit 2.
1. What types of corrosion do you know?
2. Give a definition of ground corrosion.
3. What is corrosion resistance?
4. How can artificial crevices be created?
17 . Summarize the general ideas developed in all the texts of the Unit 2.
Unit 3
MICROBIOLOGICAL CORROSION
1 . Read the international words, guess their meanings and give the Russian equivalents.
Microbiological, structural, industrial, process, microbes, biological, organism, aqueous, potential, transport, role, bacteria, anaerobic, aerobic, typical, thiobacillus, localize.
2 . Read and translate the following verbs.
To transport, to ensue, to cause, to occur, to tend, to determine, to deliver, to present, to decrease, to increase, to manifest, to settle, to be based, to engender, to reduce, to create, to operate, to perform, to penetrate, to consume, to thrive.
3 . Match the English phrases from column A with the Russian phrases in column B.
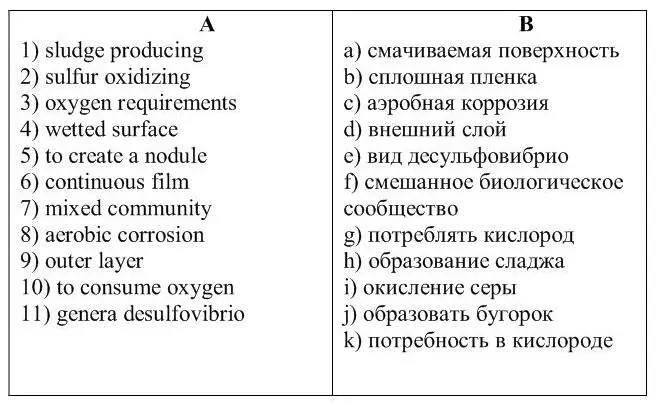
4. Read and translate the text. Summarize it in Russian.
Microbiological corrosion (MIC) refers to corrosion and ensuing loss of metal caused by biological organisms. MIC can occur in any aqueous environments and because of the present nature of microbes in fluid systems. MIC is a commonly occurring phenomenon. MIC is a common problem in industrial processes due to the presence of microbes, adequate nutrients and corrosive byproducts.
A number of metals, such as structural steels, copper alloys etc., tend to corrode generally over the entire surface in the absence of crevices or galvanic effects. In such cases, corrosion is determinated by the rate at which dissolved oxygen can be delivered to the metal surface. Biological organisms present in the aqueous medium often have the potential to increase or decrease oxygen transport to the surface; consequently, these organisms have a role in increasing or decreasing general corrosion. Most MIC, however, manifests as localized corrosion because most organisms do not form in a continuous film on the metal surface. Microscopic organisms also tend to settle on metal surfaces in the form of discrete colonies or at least spotty, rather than continuous films. Biological organisms fall under two groups based on the type of corrosion they engender: (a) anaerobic corrosion (b) aerobic corrosion. Sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) from the genera desulfovibrio are a typical example of anaerobic MIC. Aerobic sulfur oxidizing bacteria of the type thiobacillus can create an environment of up to 10 percent sulfuric acid, thereby encouraging rapid corrosion.
(From www.clihouston.com) .
5 . Read the text again. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Microbiological corrosion (MIC) refers to corrosion and ensuing alteration of metal surface caused by biological organisms.
2. Most MIC is defined as limited corrosion because most organisms do not form in a continuous film on the metal surface.
3. The type thiobacillus can form an environment of up to 70 percent ferrum acid.
6 . Work in pairs. Translate the following text from English into Russian.
MIC is not caused by a single microbe, but is attributed to many different microbes. These are often categorized by common characteristics such as by-products (i.e., sludge producing) or compounds they effect (i.e. sulfur oxidizing). In a general sense, they all fall into one of two groups based upon their oxygen requirements; one being aerobic (requires oxygen) such as sulfur oxidizing bacteria, and the other being anaerobic, (requires little or no oxygen), such as sulfate reducing bacteria.
General corrosion affects the entire surface or at least the wetted surface. MIC, on the other hand, is very localized. It creates a nodule and a pit beneath the nodule. There can be only a few nodules or there can be many. Within these nodules microbes rarely work alone but operate as a mixed community of differing types and groups. The different microbes perform different functions within the community. This interaction allows a community to thrive in environments that are actually hostile to some of its members. For example, in an aerobic environment, anaerobic bacteria are generally inhibited or killed. But within a community the aerobic bacteria reside in the outer layer of the nodule consuming the oxygen in the water as it penetrates the nodule. Thus, the inner portion of the nodule experiences a reduced oxygen level allowing anaerobic bacteria to thrive.
7. Read the text. What is its main idea?
Почва является вместилищем необычайно обильной и разнообразной микрофлоры, представленной многочисленными группами бактерий, плесневыми грибками, дрожжевыми организмами и т. п.
Количество разнообразных бактерий, приходящееся на 1 грамм почвы, достигает сотен миллионов, а иногда и десятков миллиардов. Основная масса микроорганизмов встречается в верхних горизонтах почвы, однако и в подпочвенных слоях они содержатся в значительном количестве. В некоторых случаях эти организмы могут вызывать интенсивную коррозию, получившую наименование микробиологической коррозии.
Действие микроорганизмов сводится или к непосредственному влиянию на скорость анодной и катодной реакций, или к созданию коррозийной среды.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:









