Тимур Машнин - Разработка Android-приложений с Augmented Reality
- Название:Разработка Android-приложений с Augmented Reality
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:неизвестно
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:9785448380907
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Тимур Машнин - Разработка Android-приложений с Augmented Reality краткое содержание
Разработка Android-приложений с Augmented Reality - читать онлайн бесплатно ознакомительный отрывок
Интервал:
Закладка:
private GoogleMap mMap;
private GoogleMapWorldPlugin mGoogleMapPlugin;
private World mWorld;
@Override
protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super. onCreate (savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.map_google);
Button myLocationButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.myLocationButton);
myLocationButton.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
myLocationButton.setOnClickListener (this);
((SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager () .findFragmentById(R.id.map)).getMapAsync (this);
}
@Override
public boolean onMarkerClick (Marker marker) {
// To get the GeoObject that owns the marker we use the following
// method:
GeoObject geoObject = mGoogleMapPlugin.getGeoObjectOwner (marker);
if (geoObject!= null) {
Toast.makeText (this, «Click on a marker owned by a GeoOject with the name: " + geoObject.getName (),
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show ();
}
return false;
}
@Override
protected void onResume () {
super. onResume ();
// When the activity is resumed it is time to enable the
// BeyondarLocationManager
BeyondarLocationManager. enable ();
}
@Override
protected void onPause () {
super. onPause ();
// To avoid unnecessary battery usage disable BeyondarLocationManager
// when the activity goes on pause.
BeyondarLocationManager. disable ();
}
@Override
public void onClick (View v) {
// When the user clicks on the button we animate the map to the user
// location
LatLng userLocation = new LatLng(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ());
mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom (userLocation, 15));
mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null);
}
@Override
public void onMapReady (GoogleMap googleMap) {
mMap=googleMap;
// We create the world and fill the world
mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this);
// As we want to use GoogleMaps, we are going to create the plugin and
// attach it to the World
mGoogleMapPlugin = new GoogleMapWorldPlugin (this);
// Then we need to set the map in to the GoogleMapPlugin
mGoogleMapPlugin.setGoogleMap (mMap);
// Now that we have the plugin created let’s add it to our world.
// NOTE: It is better to load the plugins before start adding object in
// to the world.
mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin);
mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this);
mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15));
mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null);
// Lets add the user position to the map
GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l);
user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ());
user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag);
user.setName («User position»);
mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user);
BeyondarLocationManager.addWorldLocationUpdate (mWorld);
BeyondarLocationManager.addGeoObjectLocationUpdate (user);
// We need to set the LocationManager to the BeyondarLocationManager.
BeyondarLocationManager
.setLocationManager ((LocationManager) getSystemService (Context. LOCATION_SERVICE));
}
}
package com.beyondar. example;
import android. os. Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.beyondar.android.plugin. googlemap. GoogleMapWorldPlugin;
import com.beyondar.android.world.GeoObject;
import com.beyondar.android. world. World;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory;
import com.google.android.gms.maps. GoogleMap;
import com.google.android.gms.maps. GoogleMap. OnMarkerClickListener;
import com.google.android.gms.maps. OnMapReadyCallback;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker;
public class GoogleMapActivity extends FragmentActivity implements OnMarkerClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback {
private GoogleMap mMap;
private GoogleMapWorldPlugin mGoogleMapPlugin;
private World mWorld;
@Override
protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super. onCreate (savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.map_google);
((SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager () .findFragmentById(R.id.map)).getMapAsync (this);
}
@Override
public boolean onMarkerClick (Marker marker) {
// To get the GeoObject that owns the marker we use the following
// method:
GeoObject geoObject = mGoogleMapPlugin.getGeoObjectOwner (marker);
if (geoObject!= null) {
Toast.makeText (this, «Click on a marker owned by a GeoOject with the name: " + geoObject.getName (),
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show ();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void onMapReady (GoogleMap googleMap) {
mMap=googleMap;
// We create the world and fill the world
mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this);
// As we want to use GoogleMaps, we are going to create the plugin and
// attach it to the World
mGoogleMapPlugin = new GoogleMapWorldPlugin (this);
// Then we need to set the map in to the GoogleMapPlugin
mGoogleMapPlugin.setGoogleMap (mMap);
// Now that we have the plugin created let’s add it to our world.
// NOTE: It is better to load the plugins before start adding object in to the world.
mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin);
mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this);
mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15));
mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null);
// Lets add the user position
GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l);
user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ());
user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag);
user.setName («User position»);
mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user);
}
}
После запуска приложения на Android устройстве появится список с примерами.
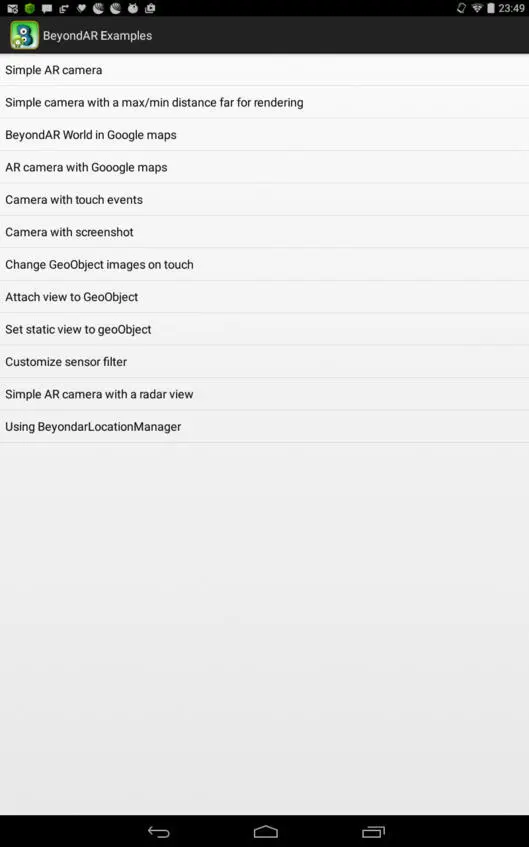
Simple AR camera – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры. При этом изображения расположены в пространстве вокруг устройства.
Simple camera with a max/min distance far for rendering – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с возможностью регулировки расстояния до изображений.
BeyondAR World in Google maps – показывает набор изображений на карте.
AR camera with Google maps – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с кнопкой переключения на карту.
Camera with touch events – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, а также сообщение при нажатии на одном из изображений.
Camera with screenshot – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с кнопкой скриншота.
Change GeoObject images on touch – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, которые заменяются на другие изображения при нажатии.
Attach view to GeoObject – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с добавлением вида к изображению при нажатии.
Set static view to geoObject – вместо изображений показывает виды на фоне камеры, а также сообщение при нажатии на одном из видов.
Customize sensor filter – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с возможностью регулировки чувствительности датчика ориентации.
Simple AR camera with a radar view – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, а также расположение изображений вокруг устройства.
Using BeyondarLocationManager – показывает набор изображений на карте с кнопкой обновления местоположения.
Для работы BeyondAR фреймворка в файле манифеста приложения декларируются необходимые разрешения и наличие сенсоров устройства.
android: layout_width=«match_parent»
android: layout_height=«match_parent»
android: id="@+id/parentFrameLayout»>
android: id="@+id/beyondarFragment»
android:name="com.beyondar.android.fragment.BeyondarFragmentSupport»
android: layout_width=«match_parent»
android: layout_height=«match_parent» />
Далее создается объект World – контейнер объектов дополненной реальности, который затем добавляется во фрагмент BeyondarFragmentSupport.
Метод mBeyondarFragment.showFPS (true) показывает количество кадров в секунду в левом верхнем углу экрана.
Вся магия по созданию объектов дополненной реальности осуществляется в классе CustomWorldHelper.
Здесь создается новый контейнер World, устанавливается его местоположение в реальном мире, а также на основе изображений создаются объекты GeoObject, которые добавляются в контейнер World.
public static World sharedWorld;
sharedWorld = new World (context);
sharedWorld.setGeoPosition (41.90533734214473d, 2.565848038959814d);
GeoObject go4 = new GeoObject (4l);
go4.setGeoPosition (41.90518862002349d, 2.565662767707665d);
go4.setImageUri("assets://creature_7.png»);
go4.setName («Image from assets»);
sharedWorld.addBeyondarObject (go4);
По умолчанию для контейнера World и для его объектов, в классе CustomWorldHelper, задаются фиксированные координаты в реальном мире. Исправим это, привязав координаты контейнера World к местоположению устройства.
Для определения местоположения устройства используем Fused location provider API (Android API Level> v9, Android Build Tools> v21).
Изменим код классов CustomWorldHelper, GoogleMapActivity и SimpleCameraActivity.
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Context;
import android. location. Location;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.beyondar.android.world.GeoObject;
import com.beyondar.android. world. World;
@SuppressLint («SdCardPath»)
public class CustomWorldHelper {
public static final int LIST_TYPE_EXAMPLE_1 = 1;
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка: