Мануэль Кёне - Колени. Как у вас дела? Как ухаживать за одним из самых уязвимых суставов и не пропустить проблемы
- Название:Колени. Как у вас дела? Как ухаживать за одним из самых уязвимых суставов и не пропустить проблемы
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Издательство:Литагент 5 редакция «БОМБОРА» (БЕЗ ПОДПИСКИ)
- Год:2022
- Город:Москва
- ISBN:978-5-04-160200-0
- Рейтинг:
- Избранное:Добавить в избранное
-
Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Мануэль Кёне - Колени. Как у вас дела? Как ухаживать за одним из самых уязвимых суставов и не пропустить проблемы краткое содержание
Мануэль Кёне приводит множество случаев из своей практики и подробно разбирает их с точки зрения причин проблемы или травмы, лечения и последствий.
Внимание! Информация, содержащаяся в книге, не может служить заменой консультации врача. Необходимо проконсультироваться со специалистом перед совершением любых рекомендуемых действий.
В формате PDF A4 сохранён издательский дизайн.
Колени. Как у вас дела? Как ухаживать за одним из самых уязвимых суставов и не пропустить проблемы - читать онлайн бесплатно ознакомительный отрывок
Интервал:
Закладка:
После того как первый прототип был утвержден главным имамом в Турции как пригодный для вероисповедания, коврик должен был пройти боевое крещение. Пирисан и его жена совершили свой первый хадж в Мекку. Все вокруг святыни Каабы выложено мрамором, что создает особенно тяжелые условия для коленей. Не только эти двое, но и несколько азиатских пар были настолько впечатлены ковриком, что не захотели расставаться с ним после тестирования. Сейчас Пирисан продает около трех тысяч ковриков в год. Помимо стандартной модели из бархата, также представлен гипоаллергенный вариант из синтетических волокон, обладающих пыле– и грязеотталкивающим эффектом, а также влагостойкостью. А за небольшую доплату предлагается оснастить коврик компасом, чтобы в непривычной обстановке повернуться точно в направлении Мекки.
Порой врачам приходят в голову причудливые идеи… В середине 1990-х годов американский ортопед доктор Скотт Ф. Дай и его коллега провели операцию на колене без наркоза. Они хотели узнать, какие структуры в колене чувствуют боль от прикосновения. Коллега оперировал доктора Дая, пока тот находился в состоянии полного бодрствования. Когда он дотронулся до хряща, Дай вообще ничего не почувствовал, прикосновение к крестообразной связке вызвало умеренную боль, а от прикосновения к так называемому жировому телу Гоффа, расположенному перед мениском, Дай едва не полез на стену. Вот его зарисовки:
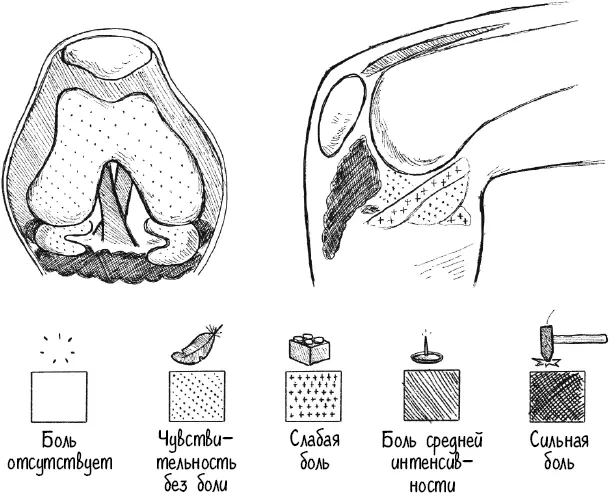
Ощущение боли при прикосновении к разным частям колена проявляется с различной интенсивностью
Библиография
1. Englund et al. (2012) Meniscus pathology, osteoarthritis and the treatment controversy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012 May 22; 8(7): 412–9.
2. Biedert RM (2000) Treatment of intrasubstance meniscal lesions: a randomized prospective study of four different methods. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 8(2): 104–108.
3. Herrlin SV et al. (2007) Arthroscopic or conservative treatment of degenerative medial meniscal tears: a prospective randomised trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15: 393–401.
4. Herrlin SV et al. (2013) Is arthroscopic surgery beneficial in treating non-traumatic, degenerative medial meniscal tears? A five year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21: 358–64.
5. Katz JN et al. (2013) Surgery versus Physical Therapy for a Meniscal Tear and Osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med 368: 1675–84.
6. Chatain F et al. (2001) The natural history of the knee following arthroscopic medial meniscectomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001; 9(1): 15–8.
7. Burks RT et al. (1997) Fifteen-year follow-up of arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. Arthroscopy 13: 673–679.
8. Gauffin H et al. (2014): Knee arthroscopic surgery is beneficial to middle-aged patients with meniscal symptoms: a prospective, randomised, single-blinded study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22: 1808–1816.
9. Herrlin SV et al. (2013) Is arthroscopic surgery beneficial in treating non-traumatic, degenerative medial meniscal tears? A five year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21: 358–64.
10. Katz JN et al. (2013) Surgery versus Physical Therapy for a Meniscal Tear and Osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med 368: 1675–84.
11. JAMA Surg. (2014) Association of High-Volume Hospitals With Greater Likelihood of Discharge to Home Following Colorectal Surgery. 149(3): 244–51.
12. Juhl C et al. (2014) Impact of exercise type and dose on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol; 66(3): 622–36.
13. Brosseau L et al. (2003): Intensity of exercise for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Cochrane Datebase Syst Rev. (2): CD004259.
14. Skou u. Roos (2017) Good Life with osteoArthritis in Denmark (GLA: D™): evidence-based education and supervised neuromuscular exercise delivered by certified physiotherapists nationwide. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders Volume 18, Article number: 72.
15. Skou u. Roos (2017) Good Life with osteoArthritis in Denmark (GLA: D™): evidence-based education and supervised neuromuscular exercise delivered by certified physiotherapists nationwide. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders Volume 18, Article number: 72.
16. Iqbal SM et al. (2016) Lubricin/proteoglycan 4 binds to and regulates the activity of toll-like receptors in vitro. Sci Rep. 6:18910.
17. Kosinska MK et al. (2015) Articular joint lubricants during osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis display altered levels and molecular species. PLoS One; 10(5): e0125192
18. Bannuru RR et al. (2016) Comparative safety profile of hyaluronic acid products for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2016 Dec; 24(12): 2022–2041.
19. Debbi EM et al. (2011) Efficacy of methylsulfonylmethane supplementation on osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled study. BMC Complement Altern Med. Jun 27; 11:50.
20. Benito-Ruiz P et al. (2009): A randomized controlled trial on the efficacy and safety of a food ingredient, collagen hydrolysate, for improving joint comfort. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 60 Suppl 2: 99–113.
21. Manoy P et al. (2017) Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Quality of Life and Physical Performance in Osteoarthritis Patients. Nutrients. Jul 26; 9(8). pii: E799.
22. Gao XR et al. (2017) The effect of vitamin D supplementation on knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg Oct; 46: 14–20.
23. Gruenwald J et al. (2009) Effect of glucosamine sulfate with or without omega-3 fatty acids in patients with osteoarthritis. Adv Ther. Sep; 26(9): 858–71.
24. Guilak F et al. (2014) Dietary fatty acid content regulates wound repair and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis following joint injury. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Nov; 74(11): 2076–2083. Published online 2014 Jul 10.
25. Rein E et al. (2004). A herbal remedy made from a subspecies of rose-hip Rosa canina, reduces symptoms of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 12 (Suppl. 2): 80.
26. Warholm O et al. (2003). The Effects of a Standardized Herbal Remedy Made from a Subtype of Rosa canina in Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. Jan; 64(1): 21–31.
27. Cisár P et al. (2008) Effect of pine bark extract (Pycnogenol) on symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. Phytother Res. Aug; 22(8): 1087–92.
28. Belcaro G et al. (2008) Treatment of osteoarthritis with Pycnogenol. The SVOS (San Valentino Osteo-arthrosis Study). Evaluation of signs, symptoms, physical performance and vascular aspects. Phytother Res. Apr; 22(4): 518–23.
29. Jamison RN et al. (1995) Weather changes and pain: perceived influence of local climate on pain complaint in chronic pain patients. Pain May; 61(2): 309–15.
30. Otto-Lambertz C et al. (2017) Periprothetische Infektionen beim Gelenkersatz. Deutsches Ärzteblatt; 114: 374–353.
31. Trampuz A. et al. (2015) Management periprothetischer Infektionen des Kniegelenks. Der Orthopäde, Springer-Verlag Heidelberg.
32. Wollmerstedt N et al. (2006) Aktivit ä tsmessung von Patienten mit H ü fttotalendoprothesen. Der Orthopäde Volume 35, Issue 12, 1237–1245.
33. Zeggini E et al. (2019) Identification of new therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank data. Nature Genetics Volume 51, 230–236.
34. Thaller PH et. al. (2018) O-Beine und intensives Fu ß balltraining im Wachstumsalter Systematisches Review und Metaanalyse. Deutsches Ärzteblatt; 115: 401–408.
35. De Cock L et al. (2018) Knee alignment in adolescents is correlated with participation in weight-bearing sports. International Orthopaedics; Volume 42, Issue 12, 2851–2858.
36. Englund M et al. (2009) Meniscal tear in knees without surgery and the development of radiographic osteoarthritis among middle-aged and elderly persons: The Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum 60: 831–9.
37. Badlani JT et al. (2013) The effects of meniscus injury on the development of knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Am J Sports Med 41(6): 1238–1244.
38. Ludwig, O. (2008): Aktuelle Ergebnisse der Kid-Check-Studie – Haltungs– und Motorikuntersuchungen an Kindern und Jugendlichen, www.kidcheck.de.
39. Dunlop D. (2014) Relation of physical activity time to incident disability in community dwelling adults with or at risk of knee arthritis: prospective cohort study. BMJ 2014; 348.
40. Anandacoomarasamy A. et al. (2009) Obesity and the musculoskeletal system. Curr Opin Rheumatol. Jan; 21(1): 71–77.
41. Bing Lu et al. (2014) Milk Consumption and Progression of Medial Tibiofemoral Knee Osteoarthritis: Data From the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) Jun; 66(6); 802–809.

Примечания
1
В Германии под физиотерапией понимается ЛФК и массаж. – Прим. ред .
2
Все имена пациентов изменены. – Прим. авт .
3
По современным данным, дегенерация и истончение межпозвонкового диска само по себе является источником боли в спине примерно в 5 % случаев. – Прим. науч. ред .
4
Автор еще не сказал про блокаду коленного сустава, которая наравне с болью является патогномоничным (характерным) признаком разрыва мениска. – Прим. науч. ред .
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:




![Анетте Яспер - Зубы. Как у вас дела? [litres]](/books/1061196/anette-yasper-zuby-kak-u-vas-dela-litres.webp)
![Андреас Штипплер - Мышцы. Как у вас дела? [litres]](/books/1064734/andreas-shtippler-myshcy-kak-u-vas-dela-litres.webp)




